Everything You Need to Know About the Endocannabinoid System
9/9/2022 1:52 PM
Everything You Need to Know About the Endocannabinoid System
Have you ever wondered why smoking weed makes you feel different than your friends? You can thank the unique workings of the endocannabinoid system for that.
Although it was discovered in the 1990s by scientists, the endocannabinoid has always been a bit of a mystery when compared to other body systems.
In this guide, we’ll discuss everything you need to know about the endocannabinoid system, including how it works, what body functions it controls, and how cannabis affects it.
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
 The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a metabolic body system composed of chemical signals and receptors that act as a bridge between the body and mind.
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a metabolic body system composed of chemical signals and receptors that act as a bridge between the body and mind.
It performs complex actions within the nervous system, the immune system, and all of the body’s organs. The body cannot be in a state of complete and total health if the endocannabinoid system is not functioning properly.
The endocannabinoid system is activated by cannabinoids that are either created naturally within the body (known as endocannabinoids) as well as the ones that are found in cannabis (known as phytocannabinoids).
Here’s a tip for remembering the difference between these compounds: “endo” refers to internal compounds while “phyto” refers to plant compounds.
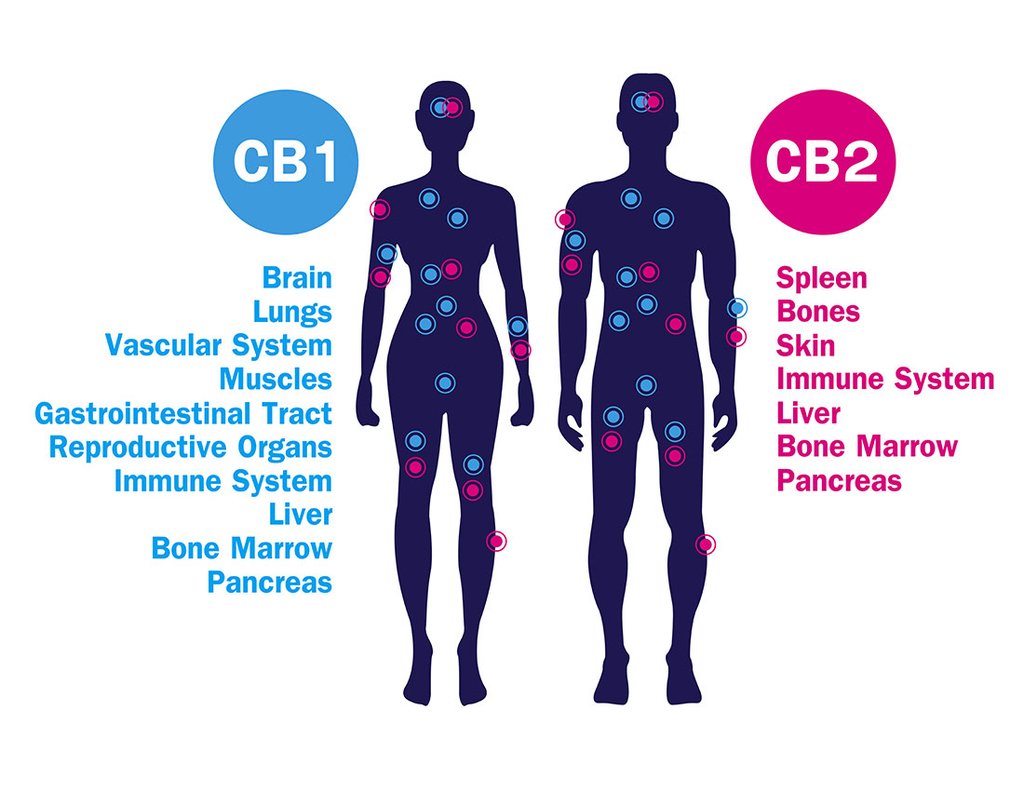
Endocannabinoid receptors are located all over the body. The brain is primarily composed of CB1 receptors that control the activity levels of neurotransmitters, which influence things like body temperature, appetite, concentration levels, mood, and hunger.
CB2 receptors are primarily located within our immune tissues. Their job is to control inflammation and regulate the immune response.
Because the majority of our immune cells reside in the gut, CB2 receptors are also responsible for influencing intestinal inflammation, contractions, regularity, and pain or other symptoms associated with IBD.
How Does The Endocannabinoid System Work?
 To understand how the endocannabinoid system works, let's take a look at an example of someone who has fallen and is in pain. When you fall and hit the ground, you feel immediate pain.
To understand how the endocannabinoid system works, let's take a look at an example of someone who has fallen and is in pain. When you fall and hit the ground, you feel immediate pain.
However, after you fall, the nervous system sends out enzymes that interrupt the pain signal so that you stop feeling pain a few minutes after falling. These enzymes work by creating endocannabinoids that help regulate the pain response.
The two main types of endocannabinoids produced are:
-
Anandamide: this compound is known as the ‘bliss molecule’ because it regulates the reward response, mood, and emotions. Low levels are linked to depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders.
-
2-Arachidonoylglycerol (also known as 2-AG): this compound is primarily responsible for regulating inflammation. It plays a large role in boosting immune health, controlling the pain response, and regulating mood, memory, and sleep.
The endocannabinoid system is in charge of regulating many responses as well as influencing the development (or prevention) of some diseases.
Essentially, it’s in charge of maintaining homeostasis within the body, meaning that it oversees a variety of processes to ensure everything is working in harmony.
Nervous system support
The autonomic nervous system has two main parts: the sympathetic and the parasympathetic systems. The sympathetic nervous system is what controls the “flight or fight” response while the parasympathetic system functions within the digestion and sleep aspects of our health.
The entire automatic system helps regulate digestion, heart rate, breathing, blood pressure, body heat, and pupil dilation.
Research shows that when there are problems within the CB1 receptors, it causes problems with learning, memory, pain, addiction, reward, neuroinflammation, degeneration, metabolism, food intake, bone mass, and more.
Problems with CB2 receptors have been linked to chronic pain, alcohol and nicotine addiction, stress, autoimmune conditions, and more.
Sleep Cycle
Sleep cycles are regulated by the body’s internal clock, which is also known as circadian rhythms. Research shows that activation of the CB1 receptors may help promote sleep.
Immune response
The endocannabinoid system has both an inhibitory and a stimulatory effect on the immune system. This is ideal for those with autoimmune conditions because it helps tame the overactive response that is responsible for activating the disease.
Research shows that activating the endocannabinoid system may help relieve symptoms of multiple sclerosis, osteoarthritis, asthma, HIV, and even cancer.
Pain signals
The endocannabinoid system helps intercept pain signals that the body sends to the brain, which can help reduce symptoms of chronic pain. It’s also responsible for regulating inflammatory responses that may contribute to pain.
Body temperature
With the help of the sympathetic nervous system, the body maintains a normal core temperature that responds to factors such as heart rate and blood pressure, allowing the body to maintain internal balance.
Sometimes, your core temperature increases when you are fighting an infection. Cannabinoids - such as THC - have been shown to reduce body temperature when you are sick.
How Does Cannabis Affect the Endocannabinoid System?
 Although the body naturally produces cannabinoids, using cannabis is an excellent way to provide the endocannabinoid system with the compounds it needs to stay properly regulated.
Although the body naturally produces cannabinoids, using cannabis is an excellent way to provide the endocannabinoid system with the compounds it needs to stay properly regulated.
Considering that there are thousands of cannabis strains and each contains its own unique cannabinoid profile, it’s hard to pinpoint how cannabis cannabinoids will affect the endocannabinoid system. The possibilities are endless, based on the ratios of receptors in the body and cannabinoid compounds in cannabis alone.
Most people find that using cannabis helps reduce general pain, fatigue, anxiety, insomnia, depression, and mood disorders. However, you’ll need to try lots of different strains to determine which is the best combination for you.
And even when you find a strain that works, keep in mind that the effects it has on you may change, depending on your body's unique chemistry and state of overall health.
Final Thoughts
The endocannabinoid system is a network of cells, organs, and chemical signals that influence a variety of body mechanisms, namely the nervous system, immune system, sleep, appetite, and pain response.
Research shows that impairments within the endocannabinoid system may lead to disease and unwanted symptoms.
Using marijuana is a good way to stimulate the endocannabinoid system and encourage the body to remain in homeostasis, but you may need to try a variety of marijuana strains to determine the best combination for you.
Have you noticed any of the above effects? Do you know anything about related biology? Please tell us about your experiences in the comments section below!







 Loading...
Loading...